Port types¶
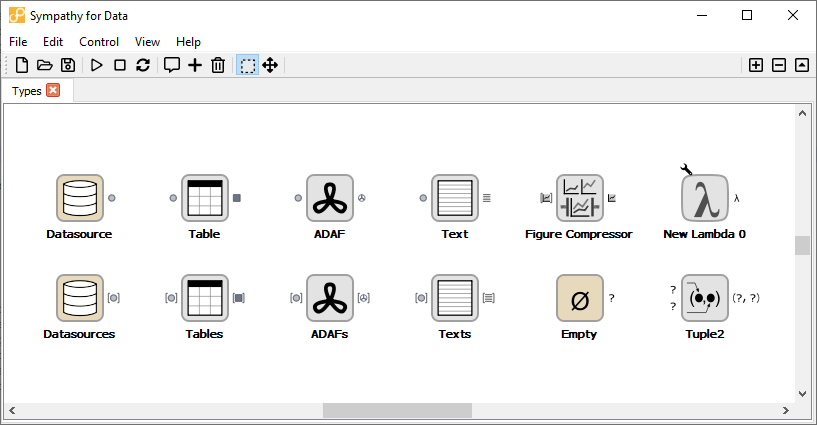
Nodes with different port types. The upper row of nodes all have single item ports whereas the nodes in the bottom row have list ports. This can be seen by the fact that those ports are enclosed by square brackets.¶
Datasource¶
The Datasource format is only used as a pointer to files or to a databases. It is often used at the start of a workflow to pinpoint the data that the workflow will be working with.
See also the nodes Datasource and File Datasources.
Table¶
Table is the most common data type when doing data analysis in Sympathy for Data. Tables can for example be found in CSV-files, Excel-files, and relational databases.
A table in Sympathy is much like a database table - a collection of columns that each have a name and contains a single kind of data (numbers, strings, dates etc.). In a table all the columns have a unique name. The supported data types for the columns are the same as for numpy arrays, with exception for the object type, np.object. A table as well as any of its columns can also be given attributes.
Ports which accept or output data with the Table type are represented by a gray square.
ADAF¶
ADAF is the data analysis format used in Sympathy when working with more complicated data. The strength of this format is that it enables the user to work with meta data (data about the data content), results (aggregated/calculated data) and timeseries (measured data) together, making advanced analysis possible in a structured way.
The different kinds of data are separated into containers. For the metadata and the results, the containers consist of a set of signals with the same structure as a Table.
For the time-resolved data, the container has a more advanced structure. The time-resolved data from a measurement can have been collected from different measurement system and the data can, because of different reason, not be stored together. For example, the two systems do not using the same sample rate or do not have a common absolute zero time. The timeseries container in the ADAF can therefore include one or many system containers. Even within a measurement system, data can have been measured with different sample rates, therefore the system container can consist of one or many rasters. Each raster consists of a time base and a set of corresponding signals and is otherwise structured like a Table.
Ports which accept or output data with the ADAF type are represented by a gray “steering wheel”.
See also Working with ADAF.
Text¶
The Text data type allows you to work with arbitrary text strings in Sympathy. Ports which accept or output data with the Text type are represented by a number of horizontal lines.
Figure¶
The Figure data type is used when creating plots.
See also Figure.
Report¶
Building a report template makes it possible to apply different sources of data several times with the same type of output.
Model (Machine Learning)¶
The (machine learning) model type includes both the algorithm and the internal data created by the algorithms which are used for machine learning.
Lists¶
Lists make it possible to handle arbitrary numbers of data together in a flow. Each list can hold only one single type of element. A good example of when lists are useful is when there are a lot of files with data and the user wants to select all the files and analyze them in a single workflow. But lists are also useful in countless other scenarios as well.
See also Item to List.
Tuples¶
Tuples represent pairs of elements. Tuples are hetrogeneous, meaning that their elements don’t have to be of the same type. One of their primary uses are for passing multiple elements to and from a Lambda.
See also Tuple.
Generic types¶
Generic types are types that can change, depending on what you connect them to. This is useful, for example, for list or tuple operations that can be performed independently of the types of the elements in the list/tuple. Examples: Item to List and Tuple. Before they are connected to anything the generic types are shown as a question mark on the port.
Function types (Lambda function)¶
Function is a datatype that represents a function that can be executed. The type is shown as the greek letter λ on the port. The corresponding tooltip when hovering, will show something like: ‘table -> table’, ‘<a> -> <a>’, where the type before the arrow is the argument type and the type after the arrow is the result type.
Graph 365¶
Sympathy Graph 365 provides access to some data from Microsoft 365 from Microsoft, using the Graph interface.
MongoDB¶
MongoDB is a document database which is supported in this toolkit by a new port type and nodes.
A document database in contrast with a SQL database deals with more unstructured or semi-structured data and does not require a fixed schema to be defined in advance. This is an advantage when the domain is not yet well known or understood or when the data model is inherently unstructured.
It stores and operates on JSON-like documents and its data format can be regarded as an extension to JSON which can be translated back and forth to JSON.
PowerBi¶
PowerBi is a data visualization and business intelligence service from Microsoft, https://powerbi.microsoft.com/.
Dataset¶
Lazy-loaded dataset.
